If you’re considering becoming a nurse, and are new to the healthcare industry, you may be wondering about the difference between practical nursing and registered nursing.
These two popular career paths within the nursing field both deal with, as the American Nurses Association (ANA) puts it, “protection, promotion, and optimization of health and abilities” and “prevention of illness and injury”, but there are distinct differences between the them. Consider the following…
Practical Nurses vs. RNs
Both Licensed Practical Nurses (LPNs) and Registered Nurses (RNs) spend the majority of their shifts focused on direct patient care, but the LPN is limited in the tasks he or she may perform in comparison to the RN. Furthermore, whereas the Registered Nurse works autonomously, the practical nurse reports directly to the RN and must work under his or her supervision.
What Practical Nurses Do
A typical shift for an LPN is likely to include some, or all of the following activities:
- Monitoring and recording patients’ vital signs
- Changing dressings
- Helping patients dress, bathe and perform exercises
- Administering medication and IV drips (not allowed in certain states)
- Collecting tissue and fluid samples for testing
- Reporting on patients’ conditions to physician or RN
It is important to note, however, that government regulations vary in each state, and limit the specific duties that practical nurses may perform within their borders. There are also varying degrees of regulation over the amount of supervision that a Licensed Practical Nurse requires.
What Registered Nurses Do
Many of the daily tasks performed by the RN are the same as those of the LPN. However, while the practical nurse’s responsibility is to properly execute each task, the RN is also accountable for patient outcomes.
In addition to the duties typically performed by an LPN, a Registered Nurse is expected to:
- Conduct diagnostic tests and analyze their results
- Formulate treatment plans for patients
- Adjust or augment existing plans as necessary
- Educate patients about their conditions and treatments
- Supervise LPNs and Certified Nursing Assistants
Registered nurses are also able to specialize in a specific field of medicine, which will further alter their duties and responsibilities.
Practical Nursing Salary vs. RN Salary
While many new professionals are initially attracted to practical nursing because of its lower barriers to entry (i.e. fewer educational requirements), the significant difference in salaries paid to LPNs and RNs often entices them to switch career paths at some point.
As the following graph illustrates, on average, Registered Nurses earn almost 60% more on an annual basis than their practical nursing peers.
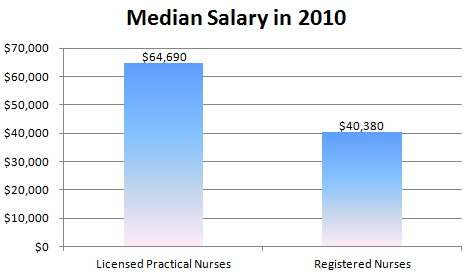
Source: www.bls.gov
This tremendous differential in pay is, obviously, the result of the greater amount of accountability held by RNs, but is also one of the largest single factors in the tremendous popularity of LPN to RN bridge programs. By enrolling in one of these courses (many of which are offered online), it is possible for current practical nurses to become eligible to sit for the NCLEX-RN in as little as one year.
Becoming an LPN vs. RN
The path to becoming a Licensed Practical Nurse is often considerably shorter than is the one for becoming an RN. Practical nursing programs generally last about one year, while becoming qualified to sit for the NCLEX-RN requires a minimum of two years schooling.
It is the ability to start one’s career quicker, and work towards the eventual goal of becoming a Registered Nurse while still earning a decent paycheck that makes the LPN path so attractive to those who are new to the nursing profession.
Which is Right for You?
The following table sums up the major pros and cons of practical nursing vs registered nursing, so you can decide for yourself which career path is for you!
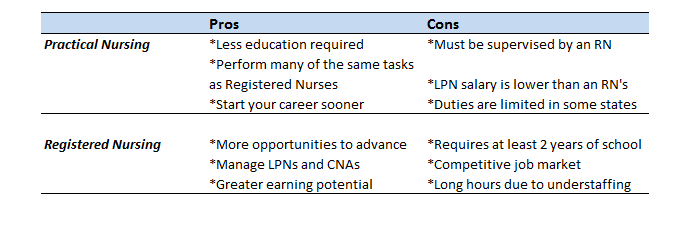
Practical Nursing vs Registered Nursing
If you’re considering becoming a nurse, and are new to the healthcare industry, you may be wondering about the difference between practical nursing and registered nursing.
These two popular career paths within the nursing field both deal with, as the American Nurses Association (ANA) puts it, “protection, promotion, and optimization of health and abilities” and “prevention of illness and injury”, but there are distinct differences between the them. Consider the following…
Practical Nurses vs. RNs
Both Licensed Practical Nurses (LPNs) and Registered Nurses (RNs) spend the majority of their shifts focused on direct patient care, but the LPN is limited in the tasks he or she may perform in comparison to the RN. Furthermore, whereas the Registered Nurse works autonomously, the practical nurse reports directly to the RN and must work under his or her supervision.
What Practical Nurses Do
A typical shift for an LPN is likely to include some, or all of the following activities:
It is important to note, however, that government regulations vary in each state, and limit the specific duties that practical nurses may perform within their borders. There are also varying degrees of regulation over the amount of supervision that a Licensed Practical Nurse requires.
What Registered Nurses Do
Many of the daily tasks performed by the RN are the same as those of the LPN. However, while the practical nurse’s responsibility is to properly execute each task, the RN is also accountable for patient outcomes.
In addition to the duties typically performed by an LPN, a Registered Nurse is expected to:
Registered nurses are also able to specialize in a specific field of medicine, which will further alter their duties and responsibilities.
Practical Nursing Salary vs. RN Salary
While many new professionals are initially attracted to practical nursing because of its lower barriers to entry (i.e. fewer educational requirements), the significant difference in salaries paid to LPNs and RNs often entices them to switch career paths at some point.
As the following graph illustrates, on average, Registered Nurses earn almost 60% more on an annual basis than their practical nursing peers.
Source: www.bls.gov
This tremendous differential in pay is, obviously, the result of the greater amount of accountability held by RNs, but is also one of the largest single factors in the tremendous popularity of LPN to RN bridge programs. By enrolling in one of these courses (many of which are offered online), it is possible for current practical nurses to become eligible to sit for the NCLEX-RN in as little as one year.
Becoming an LPN vs. RN
The path to becoming a Licensed Practical Nurse is often considerably shorter than is the one for becoming an RN. Practical nursing programs generally last about one year, while becoming qualified to sit for the NCLEX-RN requires a minimum of two years schooling.
It is the ability to start one’s career quicker, and work towards the eventual goal of becoming a Registered Nurse while still earning a decent paycheck that makes the LPN path so attractive to those who are new to the nursing profession.
Which is Right for You?
The following table sums up the major pros and cons of practical nursing vs registered nursing, so you can decide for yourself which career path is for you!